视差效果现在风靡一时,iOS7上更是使用了很多。在新的音乐App中,在iTunes Radio中,都有一种我非常喜欢的特别的视差效果。滚动的专辑封面栈。实现这个效果似乎是一个非常有趣的挑战,今天我将向你展示如何创建这个效果。当然,我们使用的是UICollectionView。下面是最终的效果。

在我开始写代码之前,我想先解释一下我的方法。我们将创建一个UICollectionViewCell,然后放置一个UIImageView在它的中间位置。这张照片是固定和等量的填充。然后我们将创建几个图像视图,每一个视图都稍微从原来的位置插入,并放在固定的图片视图后面。这些图片将根据当前单元格的滚动位置来流动,就是向左和向右移动,占据空余的空间。
这里你可以看到我描述的单元格的轮廓。蓝色的轮廓是我们固定的图片,绿色的轮廓是我们单元格的界限,而我们流动的图片用灰色轮廓标识。
接下来让我们决定这个流动图片怎么移动。我们需要知道每一个单元格相对于集合视图界限的位置。让我们创建一个通用的压缩系数来表示这个信息:
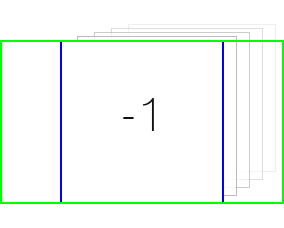
-1 代表单元格滚动到视图的右边。
0 代表单元格完美地位于视图的中间。
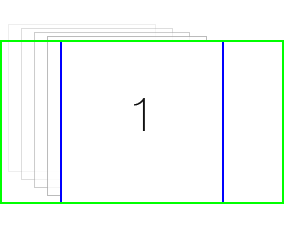
1 代表单元格滚动到视图的左边。
这称为标准化(normalization),我们可以做一个简单的线性方程:
- (CGFloat)parallaxPositionForCell:(UICollectionViewCell *)cell {
CGRect frame = [cell frame];
CGPoint point = [[cell superview] convertPoint:frame.origin toView:collectionView];
const CGFloat minX = CGRectGetMinX([collectionView bounds]) - frame.size.width;
const CGFloat maxX = CGRectGetMaxX([collectionView bounds]);
const CGFloat minPos = -1.0f;
const CGFloat maxPos = 1.0f;
return (maxPos - minPos) / (maxX - minX) * (point.x - minX) + minPos;
}
现在我们需要一个方法来在collectionView 滚动时发送这些信息给每一个单元格:
- (void)scrollViewDidScroll:(UIScrollView *)scrollView {
for (id cell in [collectionView visibleCells]) {
CGFloat position = [self parallaxPositionForCell:cell];
[cell setParallaxPosition:position]; // We will implement this next.
}
}
接下来我们需要在我们自定义的单元格类中实现setParallaxPosition:方法。这个方法将负责根据位置来移动我们的流动图片。因为我们使用通用的压缩系数,我们应该为单元格定义这些值代表什么。
-1 代表单元格滚动到视图的右边
0 代表单元格完美地位于视图的中间

1 代表单元格滚动到视图的左边
现在在我们自定义的单元格类中添加如下实现:
- (void)setParallaxPosition:(CGFloat)position {
CGRect bounds = [self bounds];
// We only use the height dimension for our image view. So the padding
// on either side will be the difference in width divided by 2.
const CGFloat padding = (bounds.size.width - bounds.size.height) / 2.0;
const CGFloat minOffsetX = -padding;
const CGFloat maxOffsetX = padding;
const CGFloat minPosition = 1.0;
const CGFloat maxPosition = -1.0;
// Compute the total offset using a linear equation
CGFloat offsetX = (maxOffsetX - minOffsetX) / (maxPosition - minPosition) * (position - minPosition) + minOffsetX;
// Divide the total offset among the images that will be moved
offsetX /= ([imageViews count] - 1);
// Apply the offsetX to each image relative to the first one
CGRect fixedRect = [[imageViews objectAtIndex:0] frame];
for (NSInteger i = 1; i < [imageViews count]; i++) {
UIImageView *imageView = [imageViews objectAtIndex:i];
CGRect imageRect = [imageView frame];
CGFloat imageWidth = imageRect.size.width;
imageRect.origin.x = CGRectGetMidX(fixedRect) - 0.5 * imageWidth + (offsetX * i);
[imageView setFrame:imageRect];
}
}
我们在这里所做的跟我们之前的非常相似。我们把位置转为-1 到 1范围内,然后转换为一个offsetX值。然后我们遍历这个流动图片视图,应用这个偏移量到每个相对于固定图片的frame上。
你可以在 Github 上查看完整的代码